How To Interpret Skewness And Kurtosis
Anders Kallner in Laboratory Statistics Second Edition 2018. Click on Options and select Skewness and Kurtosis.

Skew And Kurtosis 2 Important Statistics Terms You Need To Know In Data Science Data Science Statistics Data
There are a few general rules you can use.

How to interpret skewness and kurtosis. A standard normal distribution has kurtosis of 3 and is recognized as mesokurtic. For n 50 interpret the ShapiroWilk test. These tests can be used to make inference about any conjectured coefficients of skewness and kurtosis.
Kurtosis is a measure of the tailedness of the probability distribution. When you refer to Kurtosis you mean the Excess kurtosis ie. An absolute value of the score greater than 196 or lesser than -196 is significant at P 005 while greater than 258 or lesser than -258 is significant at P 001 and greater than 329 or lesser than -329 is significant at P 0001.
SKEWR and SKEWPR ignore any empty cells or cells with non-numeric values. In this app you can adjust the skewness tailedness kurtosis and modality of data and you can see how the histogram and QQ plot change. The mechanisms you describe--a regulatory upper limit and some tendency to exceed it--could lead either to negative or positive skew depending on the truncated distribution of the small-size fish and depending on how the fish are measured.
Tails of the distribution of data and therefore provides an indication of the presence of outliers. Kurt-3 or the outright kurtosis. A correlation between kurtosis and skewness might also be important so that not all combinations of values for theses parameters are possible.
If skewness 0 the data are perfectly symmetrical. In probability theory and statistics kurtosis from Greek. How to interpret the coefficient of skewness.
It measures the lack of symmetry in data distribution. A distribution that has a positive kurtosis value indicates that the distribution has heavier tails than the normal distribution. The frequency of occurrence of large returns in a particular direction is measured by skewness.
In the special case of normality a joint test for the skewness coefficient of 0 and a kurtosis. The outliers in a sample therefore have even more effect on the kurtosis than they do on the skewness and in a symmetric distribution both tails increase the kurtosis unlike skewness where they offset each other. But a skewness of exactly zero is quite unlikely for real-world data so how can you interpret the skewness number.
Drag and drop the variable for which you wish to calculate skewness and kurtosis into the box on the right. Using outright kurtosis I get results suggesting rejection of the null hypothesis even if I use Kurt3 Skew0 which is the ND standards stats. It is the degree of distortion from the symmetrical bell curve or the normal distribution.
As a general guideline skewness values that are within 1 of the normal distributions skewness indicate sufficient normality for the use of parametric tests. Kurtosis is a measure of whether the distribution is too peaked a very narrow distribution with most of the responses in the center Hair et al 2017 p. A symmetrical distribution will have a skewness of 0.
The skewness of the simulated data is -0008525844. For a unimodal distribution negative skew commonly indicates that the tail is on the left side of the distribution and positive skew indicates that the tail is on the right. For example when I perform the DAgostino-Pearson Test as described in the relevant section ie.
I made a shiny app to help interpret normal QQ plot. The skewness of their mass distribution would not be the same as the skewness of their length distribution. κυρτός kyrtos or kurtos meaning curved arching is a measure of the tailedness of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variableLike skewness kurtosis describes the shape of a probability distribution and there are different ways of quantifying it for a theoretical distribution and corresponding ways of.
Skewness is negative the data are negatively skewed or skewed left meaning that the left tail is longer. Endgroup whuber Jun 12 15 at 1628. Result will appear in the SPSS output viewer.
It differentiates extreme values in one versus the other tail. A distribution that leans to the right has negative skewness and a distribution that leans to the left has positive skewness. Once you know what the skewness and kurtosis of a given data sample is you need to interpret this value in a certain way.
Kurtosis provides a measurement about the extremities ie. As skewness involves the third moment of the distribution kurtosis involves the fourth moment. If the coefficient of kurtosis is larger than 3 then it means that the return distribution is inconsistent with the assumption of normality in other words large magnitude returns occur more frequently than a normal distribution.
Of three-dimensional long-run covariance matrices are needed for testing symmetry or kurtosis. For example data that follow a t-distribution have a positive kurtosis. Z Skewness Skewness-0 SE Skewness and Z Kurtosis Kurtosis-0 SE Kurtosis.
Figure 1 Examples of skewness and kurtosis. Click on Continue and then OK. A kurtosis value that significantly deviates from 0 may indicate that the data are not normally distributed.
Quick Steps Click on Analyze - Descriptive Statistics - Descriptives. There are two types of Skewness. In probability theory and statistics skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable about its mean.
The skewness value can be positive zero negative or undefined. When both skewness and kurtosis are zero a situation that researchers are very unlikely to ever encounter the pattern of responses is considered a normal distribution. Conversely you can use it in a way that given the pattern of QQ plot then check how the skewness etc should be.
Simulate 10000 samples from a normal distribution with mean 55 and standard deviation 45 then compute and interpret for the skewness and kurtosis and plot the histogram. An increased kurtosis 3 can be visualized as a thin bell with a high peak whereas a decreased kurtosis corresponds to a broadening of the peak. A negative value of skewness implies a skew to the left.

Skewness Vs Kurtosis Data Science Chart Different

Difference Between Statistical Analysis Normal Distribution Analysis

Skewed And Symmetric Distributions Statistics Math Math Foldables Data Science Learning
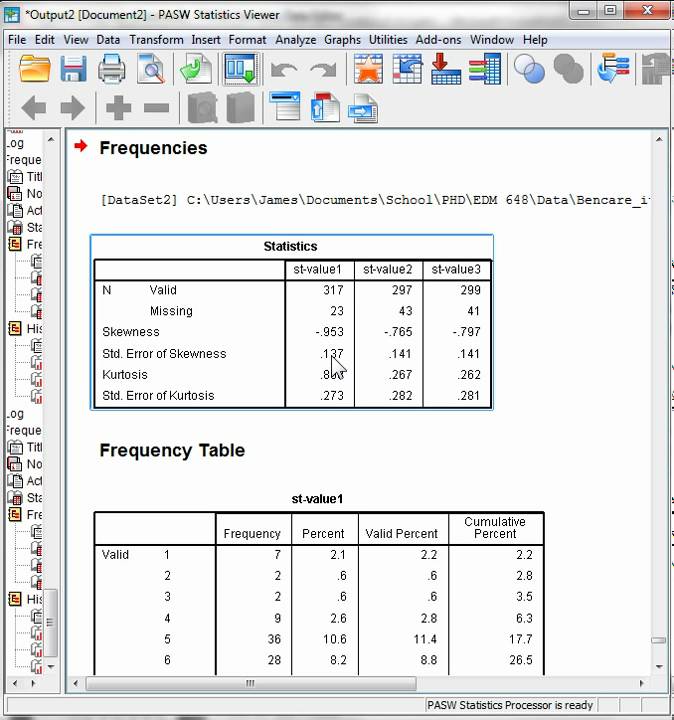
Normality Skewness And Kurtosis Graphing Data Analyze

Skewness Kurtosis Simplified Data Science Blog Help Standard Deviation

Skewness Kurtosis Data Science Learning Data Science Statistics Math

Skewness And Kurtosis A Definitive Guide Data Distribution Guide Learning

Skewness And Kurtosis Statistics Math Ap Statistics Statistics Notes

Negative Skewed A Concentration In The Low End Positive Skewed A Concentration In The High End High School Algebra School Algebra Research Methods

Skewness And Kurtosis Part 5 Examples On Pearsonian S Coefficient Of Skewness Statistics In 2021 Guided Math Knowledge Statistics

Pin By Rod Silva On Statistical Methods Data Science Learning Medical Math Data Scientist

Posting Komentar untuk "How To Interpret Skewness And Kurtosis"